What is the Difference of STEM Bridge Courses?
STEM bridge courses are designed to mitigate the challenges posed by the rigour of university level science and mathematics courses. Unlike the general prep courses, these are tailored to the STEM field and targets the learning and mental skills necessary to thrive.
The aim of summer bridge programmes is to assist students in acclimatising to the college environment. The development of bridge programmes in the fields of Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics (STEM) disciplines is expanding and gaining popularity. This is due to the more demanding nature of the curriculum and the lower persistence rates in college STEM programmes compared to other fields.
Core STEM Subjects Covered
Mathematics Foundation
- Algebra and pre-calculus concepts
- The basics and applications of calculus
- Statistical and data analytic
- Problem-solving and mathematical modelling
Physical Sciences:
- Principles of physics and techniques of laboratory work
- The basics of chemistry and chemical reactions
- Earth sciences and concepts of environment
- Designing experiments and analysing data
Life Sciences:
- Concepts of biology and cellular activities
- Basics of anatomy and physiology
- Genetics and molecular biology
- Biology of ecosystems
Engineering and Technology:
- Basic principles of engineering design
- Programming basics
- The role of technology and its use in various fields
- Thinking in systems and examining them
Research-Backed Effectiveness of STEM Bridge Programmes
Statistical Evidence of Success
Recent and detailed research proves effectiveness of STEM bridge courses and terraced courses at various levels. One such study targeted 16 STEM summer bridge programmes. On an overall first-year university grade point average, medium-size impact was (d = 0.34) and first-year university retention was (Odds Ratio [OR] = 1.747). This research shows some interesting figures:
- For bridge course participants: an improvement of 34% in first-year GPA
- For students in STEM programmes: a 75% retention rate
- For students in all STEM disciplines: improvements in all
Academic Impact over Time
This article reviews 30 different STEM bridge programmes and analyses 46 different reports over 25 years. The STEM bridge programmes focus on incomplete algebra and problem-solving techniques and barrier to student advanced STEM success in algebra and geometry gaps.
Longitudinal data indicate:
- Increased graduation rates in STEM
- Advanced coursework
- More research participation and better research
- More prepared for a graduate school
How Bridge Courses Construct Central STEM Masteries
Growth of Mathematical Proficiency
Building foundational skills: bridge courses focus on STEM algebraic gaps, and geometric reasoning, and analytical problem solving mathematics serves as the base of any STEM discipline.
Introduction of advanced concepts: Learners acquire knowledge in calculus, and differential equations and statistical techniques that will assist in the STEM fields of Physics, Chemistry, Engineering, and in research methodologies.
Understanding and solving concrete problems: students appreciate bridge programmes for real-life problem solving and mathematical models of real life and understand how Important Mathematics is to science and real life issues.
Scientific Reasoning and Critical Thinking
Hypothesis Formation and Testing: In all STEM areas, students acquire skills in forming, and analysing data, and controlled experiments and interpreting.
Data Analysis and Interpretation: Bridge courses train students on collection, and analysis, and on scientific data.
Scientific Communication: Students construct a coherent discussion on scientific developed from documents provided, focusing on reports, presentation, and data graphics.
Laboratory Skills and Experimental Techniques
Hands-on Experience: The provided laboratory sessions cover the primary techniques involved in measurement, observation, and experimentation in a variety of STEM fields.
Safety Protocols and Procedures: Students acquire crucial laboratory safety measures and are trained on proper laboratory comportment which will help them in all their STEM fields.
Technology Integration: Current Bridge programmes use computers, simulations, and more complex machines as part of the laboratory sessions. This prepares learners for the use of technology in STEM education and arms them with the requisite skills.
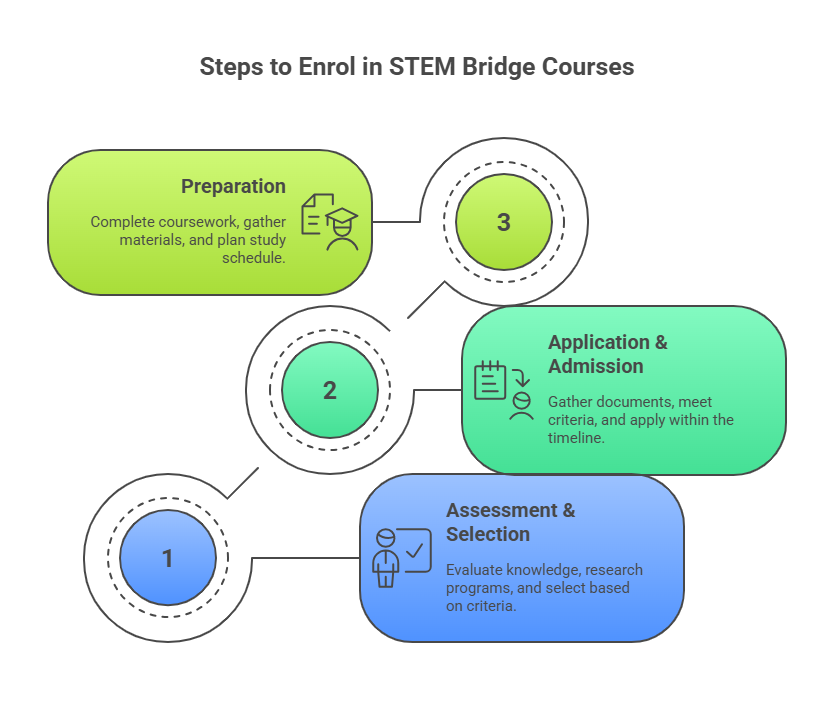
Process on How to Enrol in STEM Bridge Courses
Step 1: Assessment and Programme Selection (4-6 weeks before programme start)
Self-Assessment Phase
- How would you rate your current state of knowledge in mathematics and sciences?
- What areas of knowledge are you lacking, or which ones do you consider a weakness?
- What are the goals of the STEM field you wish to pursue and what do the universities require?
- What are the bridge programmes you can find in your local area or on the Internet?
Programme Research
- How do the programmes differ in curriculum content and/or teaching methodologies?
- What are the professional qualifications of the faculty, and what are the benchmarks that tell us about the success of the programme?
- What kinds of laboratory facilities and/or technological resources are available?
- What are the possible programme length and schedule, and what are the costs involved?
Selection Criteria
- How does the programme reflect on the intended STEM major?
- What are the instruction and student support services like?
- To what extent do students have access to laboratory sessions?
- What are the different scheduling options available?
Step 2: Application and Admission Process
What Documents are Required?
- High school transcripts, and grades that show achievements in mathematics and science
- Standardised test scores (SAT, ACT, or other similar exams)
- A personal statement that explains the goals you have set in the STEM field
- STEM recommendation letters from math and science teachers
- A filled application is to be submitted together with programme-specific essays
What are the Criteria for Admission?
- A set GPA is generally required (2.5-3.0 on average)
- Completion of the prerequisite courses in mathematics is a must
- Interest in STEM fields of any kind
- A desire to finish the programme
What is the Application Timeline?
- Start applying (3-4 months before the programme begins)
- Start applying (2-3 months before the programme begins)
- Start applying (from one month before the programme begins, space permitting)
Step 3: Preparation prior to the beginning of the programme
Academic Preparation:
- Completion of any recommended prerequisite coursework
- Self-study of the algebra of the basic sciences, along with some of the basic concepts of algebra
- Obtain a scientific calculator, and some basic computer calculation or software
- Review the recommended texts and additional materials
Logistical Preparation:
- Ensure that accommodation (if necessary) and transportation is arranged
- Obtain the necessary texts and other components for a functioning laboratory
- Set up some means of dialogue with the faculty and colleagues
- Formulate a reasonable and attainable schedule of study along with the objectives of study
Strategies for Mastering Core Subjects
Mastering Mathematics
Understanding the Concept Instead Of Rote Memorisation: Bridge courses encourage students to understand the principles of mathematics rather than memorising their formulas. They encourage students to understand how to construct equations and the logical order of the different aspects of mathematics.
Method of Problem Solving:
- Setting a timeframe for goal achievement
- Breaking the goal into smaller manageable tasks
- Identifying the applicable sub-disciplines of mathematics
- Structuring the steps in a logical order to attain the desired goal
- Validating the goal achievement and checking if the solution is plausible
Learning Mathematics: Students learn the principles of mathematics in the context of the application of mathematics in sciences like research and engineering design.
Mastery of Science Content
Connections between Disciplines: Bridge courses assist students to see the relationship across the sciences. Students see how principles of physics relate to chemistry, how chemistry relates to biology, and how all science relates to mathematics.
Experimental Design and Analysis: learners are able to frame controlled experiments, maintain proper data, and make reasonable conjectures based on experiments mastered. These skills are essential for every area in STEM.
Scientific Literacy: Bridge programmes foster learners' abilities in reading scientific documents literature, critiquing claims, and articulating science appropriately.
Conclusion
Teaching and learning of STEM Bridge Courses have been proven to be evidence-based approaches for learners to gain success in rigorous science and math courses. Through in-depth instruction, practical skills in the laboratory, and unwavering support, learners gain mastery of critical concepts and the associated cognitive skills that are pivotal for success in STEM fields.
There is data that shows evidence that being a participant in a bridge course improves your academic skills, retention rates and success in STEM career fields. Having bridge courses is indeed very useful for learners due to the fact they can determine success or failure for learner in selecting STEM programmes.
Frequently Asked Questions
Who should take STEM bridge courses?
If you feel you lack the basic skills necessary for the STEM university courses you wish to take and the underlying mathematics and science coursework. Or if you would simply like to prepare yourself for the rigors of STEM fields.
How long do STEM Bridge courses take?
Anywhere from 4 to 8 weeks during the summer to year-long intervals. Intensive summer programs usually fit within the 6 to 8 hour per day framework during the weekdays.
Is the investment for STEM bridge courses justified?
Brought to us by research: students who enrol in bridge courses enjoy STEM at higher retention and GPA levels than peers who do not take the courses. That alone makes it a worthy investment in the academic and professional future of the students.
How do online STEM bridge courses compare to in-person programs?
Online programs lack the benefits of classroom interaction as well as the physical classroom component. But if the online formats include well designed simulations, they can enhance the understanding of some STEM principles.
Do bridge courses guarantee success in STEM programs?
Although the odds of success increase remarkably with the completion of bridge courses, student effort and participation is still required. These students need to actively utilize the skills and techniques they have learned, and put in the effort to find assistance during their academic pursuits.





